7 CIO Priorities - consolidated
Chief Information Officers (CIO) of leading enterprises IOs play a pivotal role in shaping an organization’s digital future and driving innovation.
Based on personal experience working with few enterprises, here are top 7 ordered priorities. The order does change based on industry, enterprise & where in economic cycle their marketplace is.
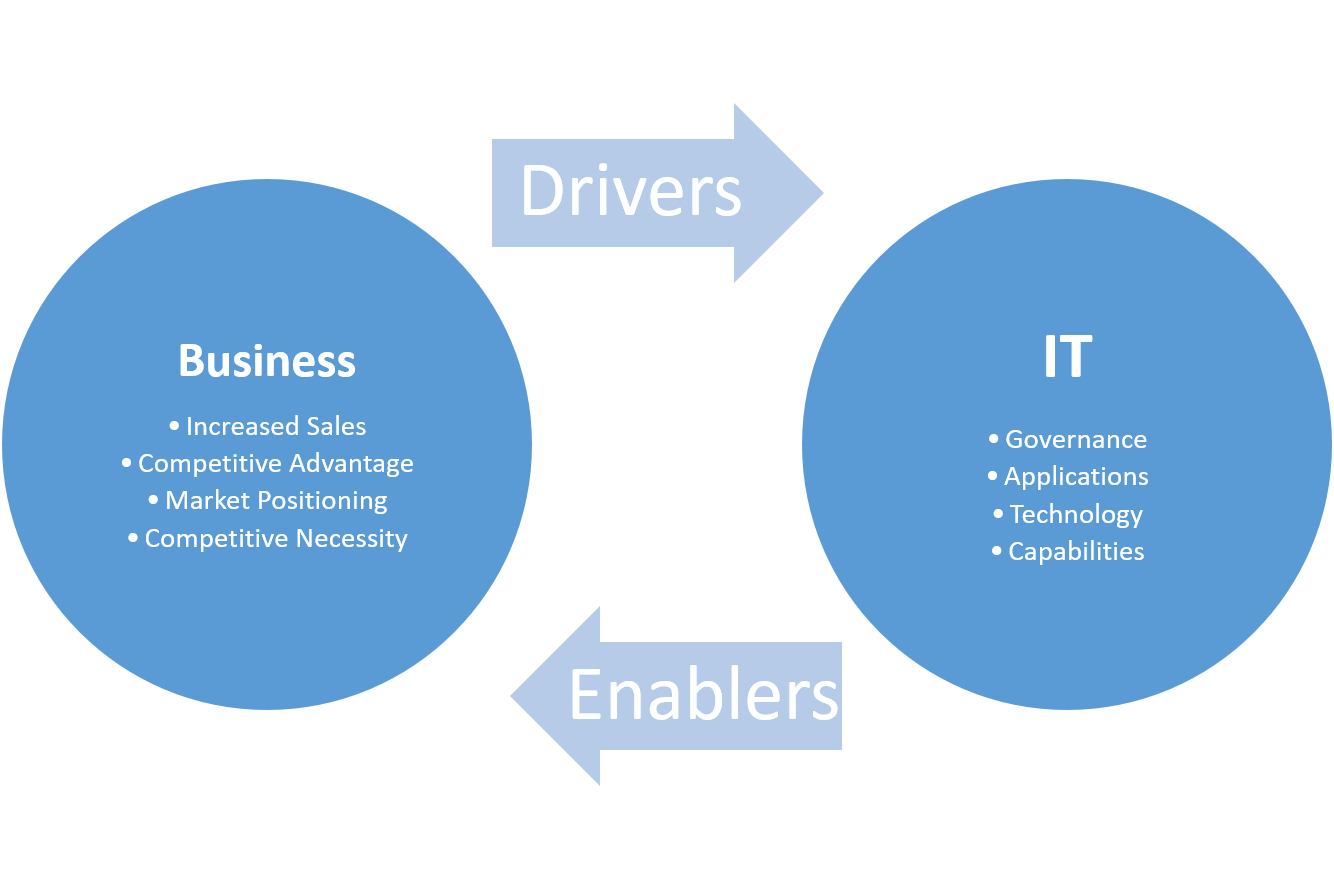
1. Align to business functionality
Enterprises with better Business-IT alignment have IT leaders that are laser focused on strategy, business process execution, innovation, new product development, and compliance. More than 30% of their time is spent with their non-IT colleagues.
Some good practices :
Define and prioritize goals/drivers better and in clear language Have SMART goals like “With same IT budget($), reduce customer churn by 10% by improving customer experience/FCR” vis-à-vis “Spend less, sell more” . Most enterprise use some form of “Business case” or “Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA)” process
Follow Agile Business demands nimble IT that deliver software faster, respond to change/feedback. And very few organization have single site agile team/s. It works on global 24x7 model
Have IT Metrics to show business the return on investments Train team for cross functional Relationships -it is people management. IT folks spending time in Business or customers shoes e.g. manning support desks, meeting end customers
Create advocates/champions for business in internal IT team e.g. Business relationship Managers (BRM) similar to IT vendor managers (VRM) who help get strategic value from suppliers
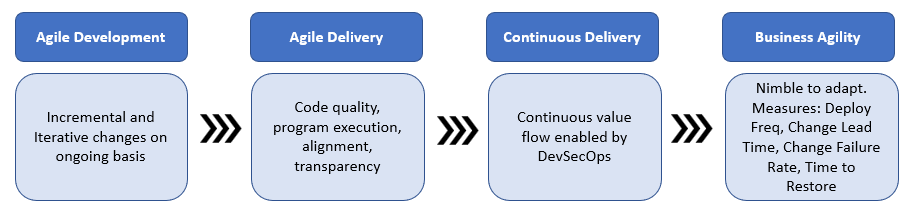
2. Achieve the agility that enterprise needs
Agile enables to deliver higher-quality software faster. It encourages close collaboration between business and IT. Agile development when combined with code quality, program execution, & continuous delivery, results in true business agility.
Smaller agile teams can be high-touch collaborative. Large enterprise agile software team are distributed (typically global). The trade-off (of co-location) is done at these large enterprises as they:
- operate in global markets,
- leverage global talent pool,
- want to contain cost.
While going agile, enterprise watch out for:
Increased speed of delivery, increased changes, do not create regular outages (otherwise continuous delivery becomes continuous pain for customers)
No tracking of what is done, where, when, how (Audit Risk – in regulated industries)
Burned out staff
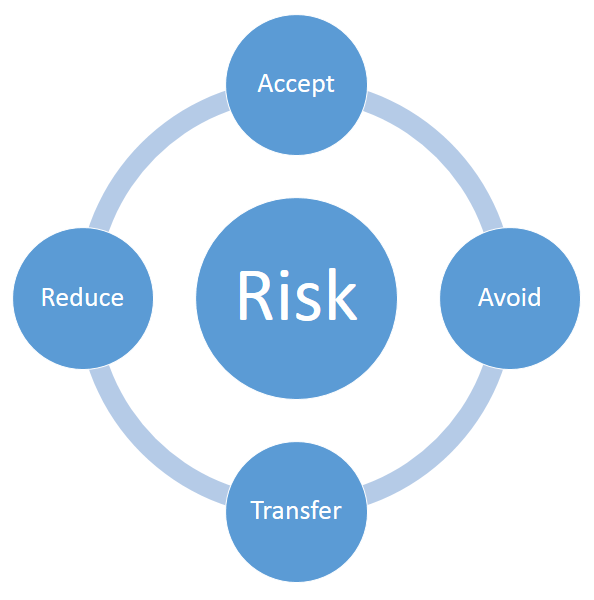
3. Mitigate risk
With proliferation of technologies, markets, mobility (form factors, Application hosting choices), Business owning Applications, Enterprise faces increased risks on all fronts – Cyber, Strategic, Reputational, Operational, Financial, and Compliance
Broadly this area is called Governance, Risk Management and Compliance (GRC). When GRC role is functionally split, it is largely across following areas – Finance & Audit GRC, Technology GRC, and Legal GRC.
Each function and its business managers need to make choices of technology/systems (ideally with CIO office involvement) to mitigate risks and ensure compliance. To understand the impact of adverse event, one needs to establish the link between technology risk scenarios and ultimate business impact.
There are several approaches that can help enterprise describe IT risk in business terms.
ISACA’s Risk IT framework does not prescribe which framework to use for risk evaluation. One of risk evaluation framework classifies four business (application) risks–Availability, Access, Accuracy, and Agility (4A Framework). Enterprise needs to also build (& continuously evolve) in 3 core disciplines – technology foundation, risk governance process, and risk aware culture.
NIST helps organizations to better understand and improve their management of cybersecurity risk. Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) provides guidance to industry, government agencies, and other organizations to manage cybersecurity risks -to better understand, assess, prioritize, and communicate its cybersecurity efforts.
Executed well, enterprise builds effective risk management capability, and derives strategic business value.
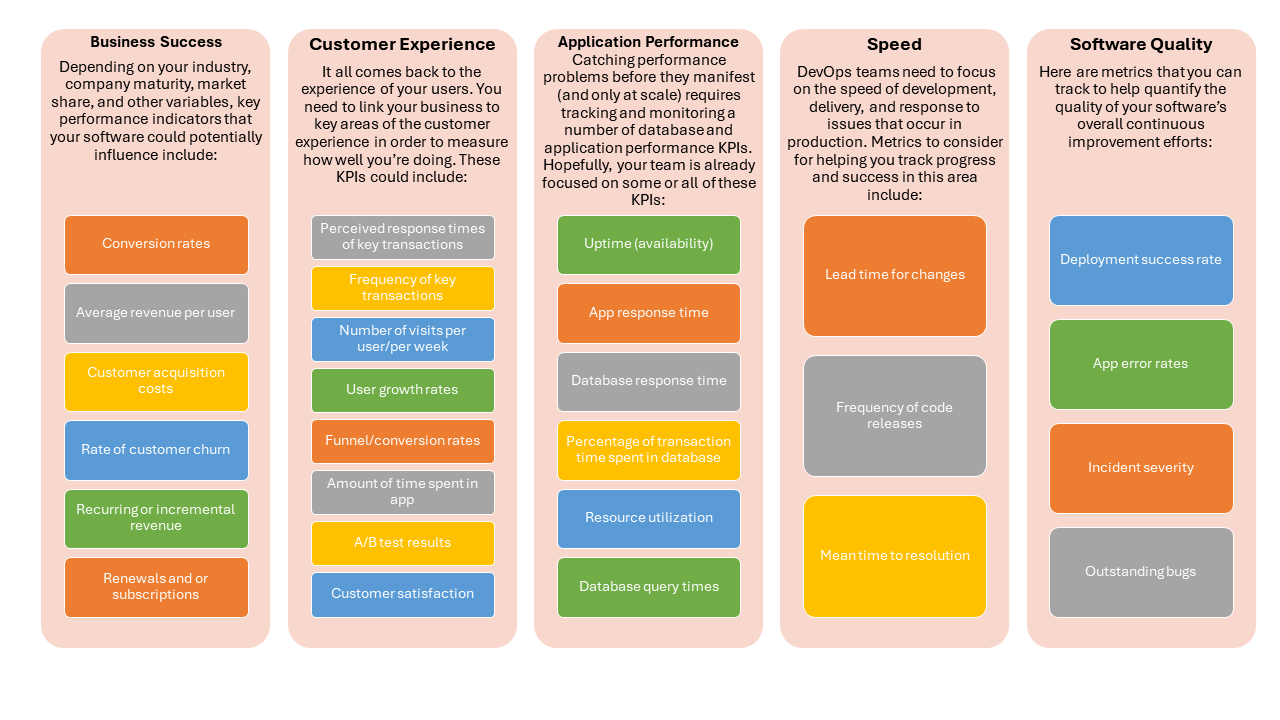
4. Raise performance levels
Most of the CIO organization have an ongoing performance management system (aka metrics), that establish standards of measurement by which performance, progress, quality, compliance can be assessed. These are both qualitative and quantitative.
Technology consulting companies with their plethora of Certifications like ISO, CMMi, have a deep-seated culture of ‘measuring and improving’ and can help bring ideas as external agents.
Most Enterprise measure around 3 major areas:
Operational Service Levels: these capture the performance of existing infrastructure, applications, and business processes. At minimum, it must capture data on availability, reliability, cost, and quality of operational execution. Value from operations typically comes from improving performance to acceptable levels.
Project Level: classic triple constraint of time, budget, and scope. Mature Enterprise/s has an effective process to assess the business value realized from the projects.
Innovation: Are mostly firm specific, such as incorporating new technology in the IT infrastructure, enabling new business models, facilitating new product features, transforming business processes,‘% revenue from new product/s, skills & capability building.
5. Stay ahead of the curve
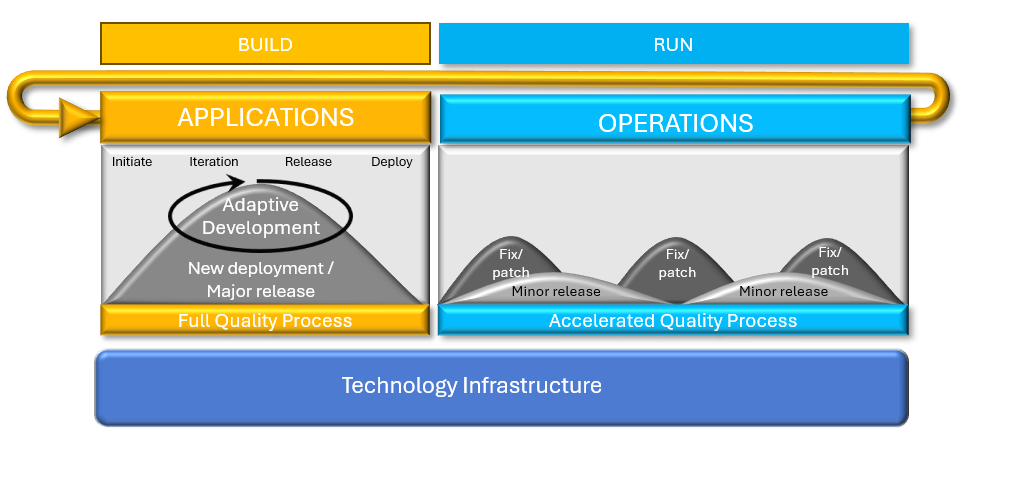
Gartner defines Bimodal as the practice of managing two separate but coherent styles of work: one focused on predictability; the other on exploration.
Mode 1 or Run, is optimized for areas that are more predictable and well-understood. It focuses on exploiting what is known, while renovating the legacy environment into a state that is fit for a digital world. Traditionally this was the Keeping-the-lights-on (KTLO), and consumes majority of budget.
Mode 2 or Build is exploratory, experimenting to solve new problems and optimized for areas of uncertainty. These initiatives often begin with a hypothesis that is tested and adapted during a process involving short iterations, potentially adopting a minimum viable product (MVP) approach. Traditionally this was the innovation part of budget.
Both modes are essential to create substantial value and drive significant organizational change, and neither is static
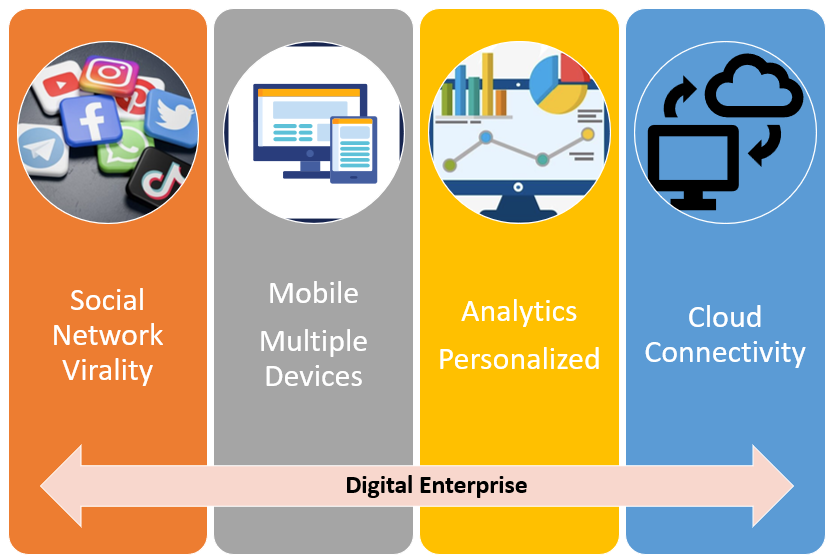
The shift of enterprise focus to growing revenues, is making it imperative to become Digital/Platform Company. Each enterprise is re-imagining its marketplace. It is becoming more interactive with customers/partners, mobile, and driving its business by analytics.
Today, SMAC (Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) enables to Re-imagine your enterprise. Call it Digital Enterprise, API Economy, Platform Company, Internet of Things, at business level, it is network ecosystem with Virality, enabled by SMAC i.e. Software.
Examples of few New Age Digital/Platform Companies:
Nike+ – A Shoe / Apparel Company is now an ecosystem of digital products and experiences designed to measure, motivate and empower you to improve
Google Wallet – A Platform that helps you Shop, Save, Pay.. with your phone… Imagine the traditional competitors that it will envelope
Personal Hygiene – A connected electric toothbrush, designed to track brushing habits and encourage better dental
International Phone Calls – Skype now accounts for third of international call volume…
Learning – MOOC’s platforms like Coursera, Khan Academy
Product Manufacturing – Shapeways, a spinoff of Philips Electronics provides a platform to 3D Print everything on-demand, which means that every order is customized and personalized
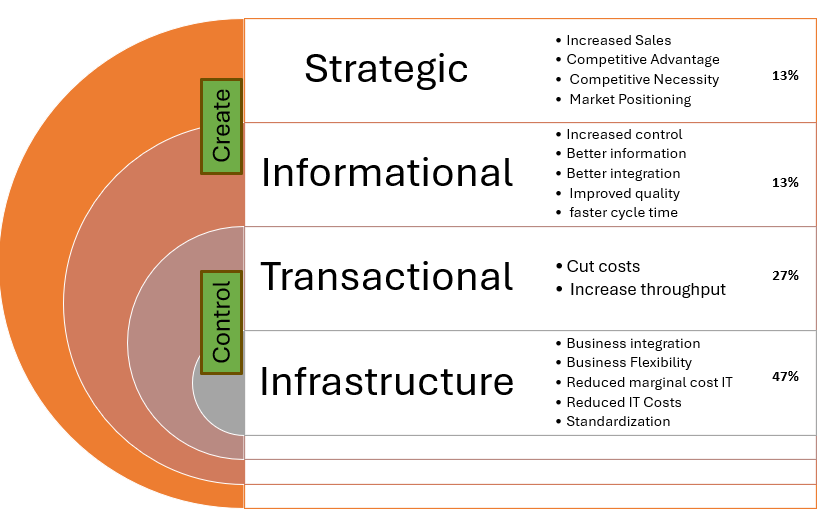
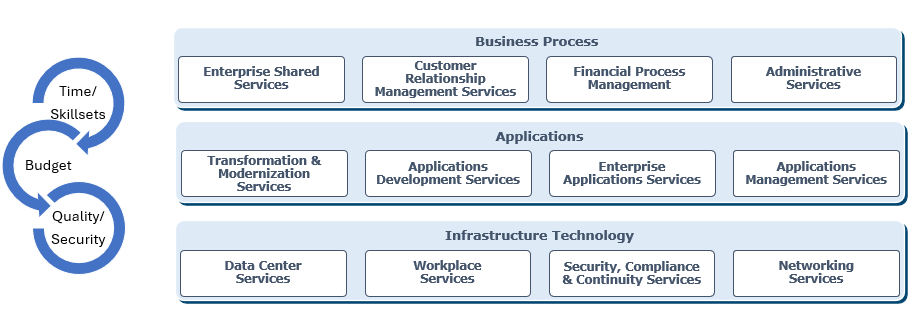
6. Find right balance between cost, quality, and speed
Typical organization spends 70%-75% of its technology budget on 2 areas: Infrastructure technology (foundational) and transaction technology (business operations, running processes).
Best practices
- Technology Portfolio Rationalization
- Running lesser number of applications, reduces maintenance/operating costs
- Moving more applications to public cloud infrastructure, takes advantage of volume/utility based pricing
- Modern App Stack/Cloud native results in business agility
- Reduced risk of legacy apps, reduce risk of excessive batch windows, more real time operational view of business
- Evolve from ‘Systems of Record’ to ‘Systems of Engagement’
- Transactional technology provides Applications/Info systems to process Quote to Cash, Procure to Pay, the core processes which bring cash flow to enterprise. Use Managed Services-based to achieve:
- Year on year productivity improvements (Cost Containment)
- Use Global Delivery model & leverage wage arbitrage (Cost Reduction)
- IT outsourcing is a strategic practice where companies entrust specific IT functions or tasks to external service providers. This cost-effective approach allows organizations to tap into specialized expertise, reduce operational overhead, and focus on core business activities